Periodontal & Dental Implant Services
Dental Implants
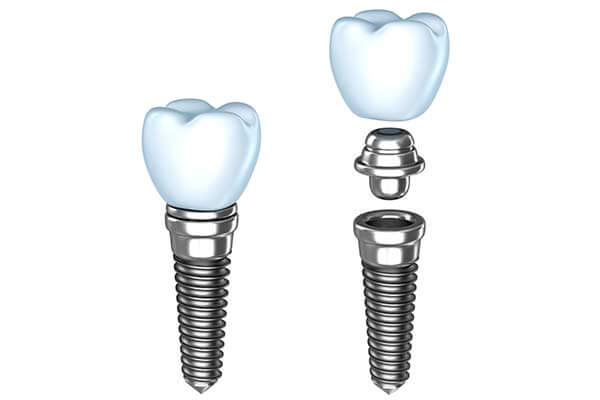
Dental implants are used to replace missing teeth and roots. Implants are small titanium posts that are surgically placed into the jawbone where the teeth are missing. The bone bonds with the titanium, acting as a tooth root substitute. Posts are attached to the implant allowing for dental prosthetic attachments.
Surgical Periodontal Procedures
Nerve Repositioning
Nerve repositioning may be an option for patients whose inferior alveolar nerves, located near the lower molars, are in the path of a potential implant. Nerve repositioning is most frequently needed when there is insufficient bone height at the desired implant site. This procedure moves the nerve out of the way of the potential implant, allowing for optimal positioning of the implant.
Gum Grafting
Commonly used to treat root exposure resulting from receded gum tissue. Tissue is removed from the roof of the mouth or from gum tissue near the tooth and stitched into the area needing gingival repair.
Bone Grafting
The replacement or enhancement of bone around teeth. When a tooth is lost, the surrounding bone collapses. Bone grafting is performed to reverse bone loss or enhance bone. The bone can be taken from parts of the body or from synthetic material. Bone grafting allows for proper support of dental implants or prostheses.
Socket Preservation
Socket preservation is a procedure performed after an extraction to reduce bone loss. Bone grafting material or bone growth enhancing elements are placed in the socket where the extracted tooth was to prevent resorption of bone.
Bone Regeneration
This procedure is used to regenerate lost bone around existing teeth, or in an area where teeth have been extracted. This procedure is often performed to protect your existing teeth and the tissues that keep them in place from bacterial plaque. The gingival tissue is folded back to remove the disease-causing bacteria. Membranes, bone grafts or tissue-stimulating proteins can be used to encourage the body's natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue.
Ridge Preservation
Involves placing a regenerative bone grafting material into empty tooth sockets to rebuild bone where an extraction has left an empty, weakened area. This process encourages your body’s natural capacity to regenerate bone.
Bite Adjustment
Even distribution of force during biting is an important aspect of oral health. If there are misalignments of the teeth affecting the bite, loose teeth, tight muscles and headaches, and tooth sensitivity or even teeth chipping can result. The bite can be checked through a number of techniques. The adjustments are made using a specialized dental instrument and the procedure is usually painless. As the muscles begin to relax, there will be changes to the bite over time. For this reason, a series of appointments are usually needed until the bite gradually adjusts and symptoms lessen or disappear altogether.
Treatments Sometimes Used in Conjunction with an Occlusal Adjustment:
Hawley Bite Plane - This is a custom removable appliance that can be useful to relieve headaches and to reduce movement of teeth that that have become loose as a result of repeated tooth grinding.
Splinting - This is a temporary solution that can help stabilize loosened teeth by securing them to neighboring teeth through the use of a Kevlar material called Ribbond to form a splint.
Medication - Anti-inflammatory medications or muscle relaxers may provide some relief for tight jaw muscles.
Osseous Surgery
A surgical procedure used to smooth and reshape affected bone under the gum tissue. This procedure is performed when a pocket around a tooth (or teeth) has not responded to other treatments. It creates a shallow pocket making it difficult for bacteria to survive and damage bone, resulting in bone loss and ultimately, tooth loss.
Bone Morphogenic Protein
Bone Morphogenic Protein is a growth factor used to stimulate bone growth. It can be used to combat jaw bone resorption or supplement bone to accommodate an implant.
Ridge Augmentation
Adequate bone volume of the jawbone is necessary for the secure placement, stability, function, aesthetics and longevity of implants. Because tooth loss can result in diminished bone volume in the jawbone, a bone expansion procedure may be necessary prior to implant placement. This procedure can increase the height and/or width of the jaw ridge through the use of mechanical manipulation combined with a bone graft. The ridge augmentation takes several months to mature and be sufficiently strong for the placement of implants. Ridge augmentation not only improves the function of implants, but is also a key contributor to the enhanced aesthetics, filling in the face around the gums and jaw and thus minimizing the appearance of aging.
Sinus Augmentation
A sinus augmentation, or sinus lift, is a surgery that adds bone to your upper jaw in the premolar and molar areas of your mouth. To add bone, an incision is made where the premolar and molar teeth were previously. Once the bone is exposed, a small circular shape is made in the bone to access the sinus. Once the sinus is accessed, the sinus membrane is gently pushed up and away from the upper jaw. Then bone graft material is filled into the space where the sinus was previously. When the bone is in place, the incision is closed and the healing process begins.
Gingivectomy
Gum reshaping or contouring is a procedure performed to reshape the gums if they rest too low or too high on your teeth. In order to reshape the gum tissue, a line is drawn to mark the new gum line. Once approved, anesthesia is applied to the area and the contouring begins. Then, a dental instrument (typically a scalpel or laser) is used to reshape the gum tissue and trim away any extra tissue overhanging the tooth.
Frenectomy
A frenectomy is a simple surgical procedure performed to release the connection of the “frenum,” a connective muscle between two tissues. There are two types of oral frenectomies that are frequently performed on both adults and children for a variety of reasons.
A labial frenectomy is performed on the tissue that connects the lip to the gums. This may be performed on children or adults to aid with orthodontic treatment or even help with the proper fitting for a denture or appliance.
A lingual frenectomy may also be referred to as the release of tongue-ties (ankyloglossia). This procedure is performed on the connective tissue under the tongue. The procedure is often performed on neonatal patients to assist with nursing or on toddlers or older patients who need the surgery to help correct speech issues caused by limited movement due the the frenum.
Conservative Periodontic Procedures
Oral Cancer Exam
During your maintenance visits we will perform and oral examination as well as a dental cleaning. During an oral examination, a visual inspection is performed to detect normal and abnormal structures of the entire mouth, head and neck. Along with radiographs, an examination detects cavities, abnormalities in existing dental restorations, gum and bone recession and any other abnormal findings within the mouth, head and neck.
Oral Prophylaxis (Teeth Cleaning)
A dental cleaning, also known as an oral prophylaxis, is the removal of dental plaque and tartar (calculus) from the teeth. Specialized instruments are used to gently remove these deposits without harming the teeth. First, an ultrasonic device that emits vibrations and is cooled by water is used to loosen larger pieces of tartar. Next, hand tools are used to manually remove smaller deposits and smooth the tooth surfaces.
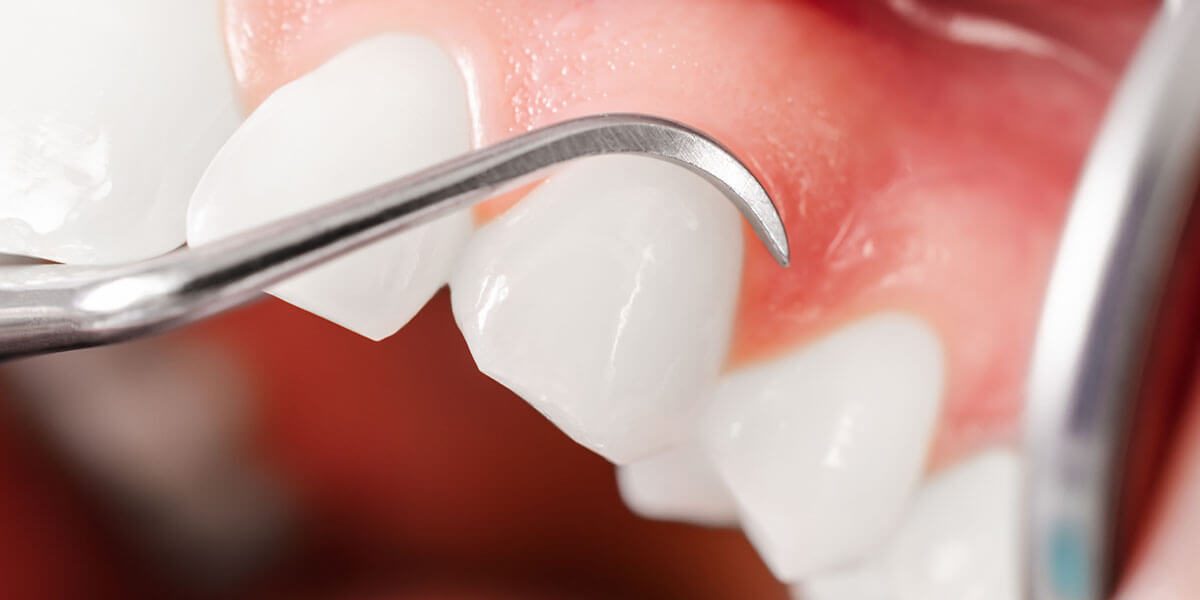
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical procedure used to treat gum disease. During the scaling process, specialized dental instruments are used to remove dental plaque and calculus from beneath the gums. Planing is the procedure used to smooth the tooth's root after the scaling process. Root planing helps the gums heal and reattach themselves to a cleaner and smoother root surface.
Crown Lengthening
Commonly used to expose more tooth structure, crown lengthening involves the removal of gum tissue and/or bone to expose more of a tooth's structure.